C Program to Add Two Integers
In this program, user is asked to enter two integers. Then, the sum of those two integers is stored in a variable and displayed on the screen.

To understand this example, you should have the knowledge of following C programming topics:
Program to Add Two Integers
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int firstNumber, secondNumber, sumOfTwoNumbers;
printf("Enter two integers: ");
// Two integers entered by user is stored using scanf() function
scanf("%d %d", &firstNumber, &secondNumber);
// sum of two numbers in stored in variable sumOfTwoNumbers
sumOfTwoNumbers = firstNumber + secondNumber;
// Displays sum
printf("%d + %d = %d", firstNumber, secondNumber, sumOfTwoNumbers);
return 0;
}Enter two integers: 12 11 12 + 11 = 23In this program, user is asked to enter two integers. Two integers entered by the user is stored in variables firstNumber and secondNumber respectively. This is done using
scanf() function.Then, variables firstNumber and secondNumber are added using + operator and the result is stored in sumOfTwoNumbers.
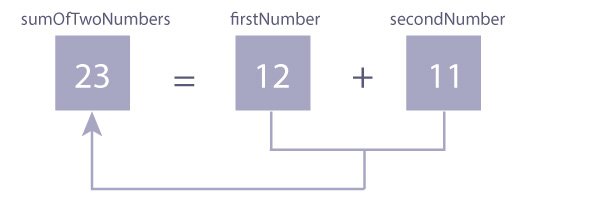
Finally, the sumofTwoNumbers is displayed on the screen using
printf() function.
Comments
Post a Comment