C Program to Compute Quotient and Remainder
This program evaluates the quotient and remainder when an integer is divided by another integer.
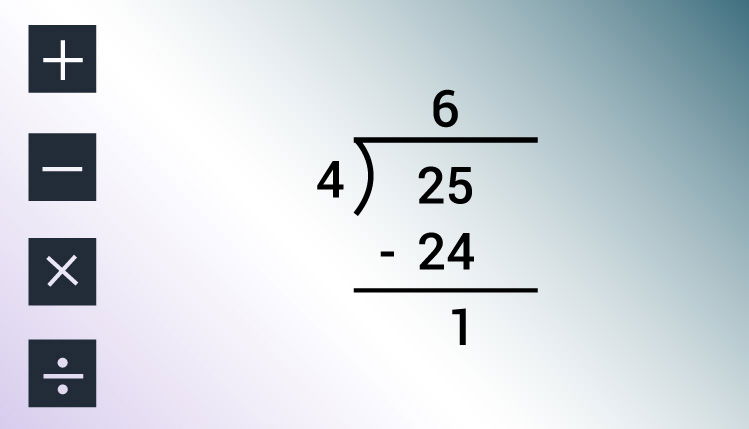
To understand this example, you should have the knowledge of following C programming topics:
Program to Compute Quotient and Remainder
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int dividend, divisor, quotient, remainder;
printf("Enter dividend: ");
scanf("%d", ÷nd);
printf("Enter divisor: ");
scanf("%d", &divisor);
// Computes quotient
quotient = dividend / divisor;
// Computes remainder
remainder = dividend % divisor;
printf("Quotient = %d\n", quotient);
printf("Remainder = %d", remainder);
return 0;
}Enter dividend: 25 Enter divisor: 4 Quotient = 6 Remainder = 1In this program, user is asked to enter two integers (dividend and divisor) which is stored in variable dividend and divisor respectively.
Then the quotient is evaluated using division / operator and stored in variable quotient.
Finally, the quotient and remainder are displayed using
printf() function.
Comments
Post a Comment